Japan –
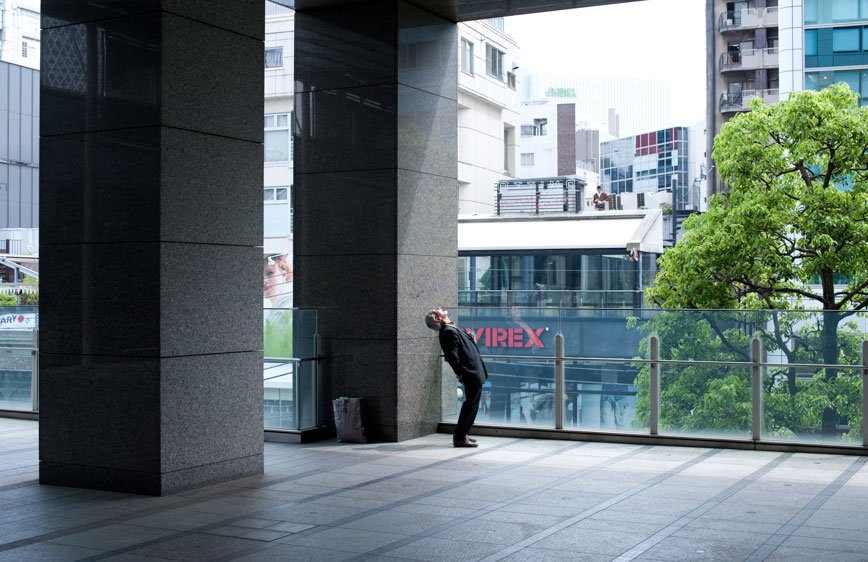
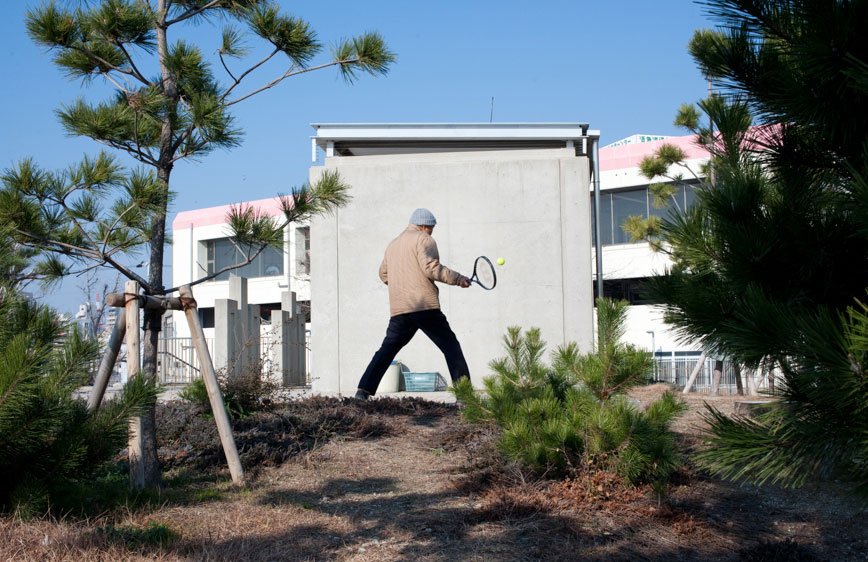
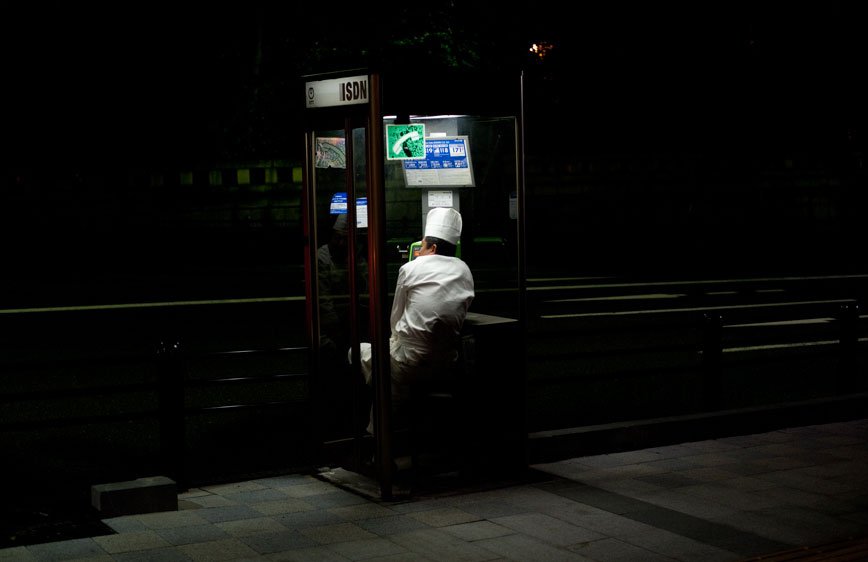
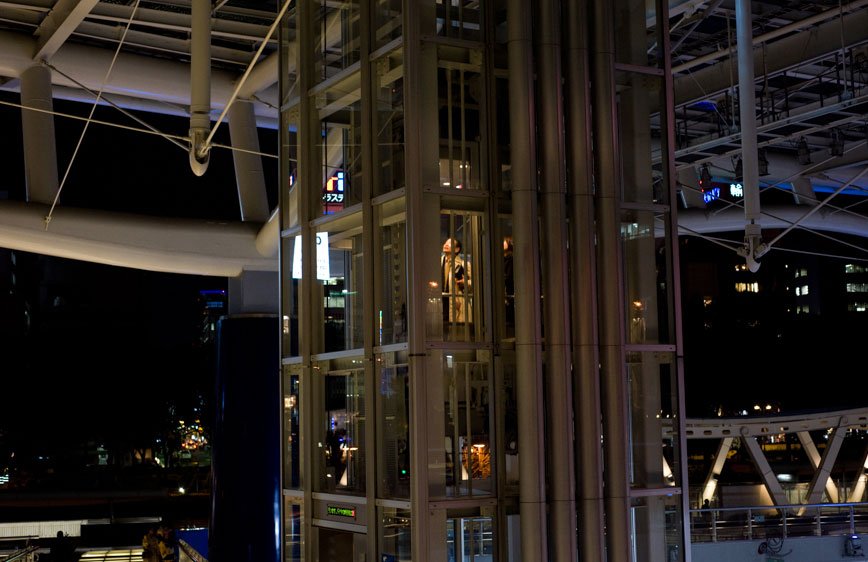
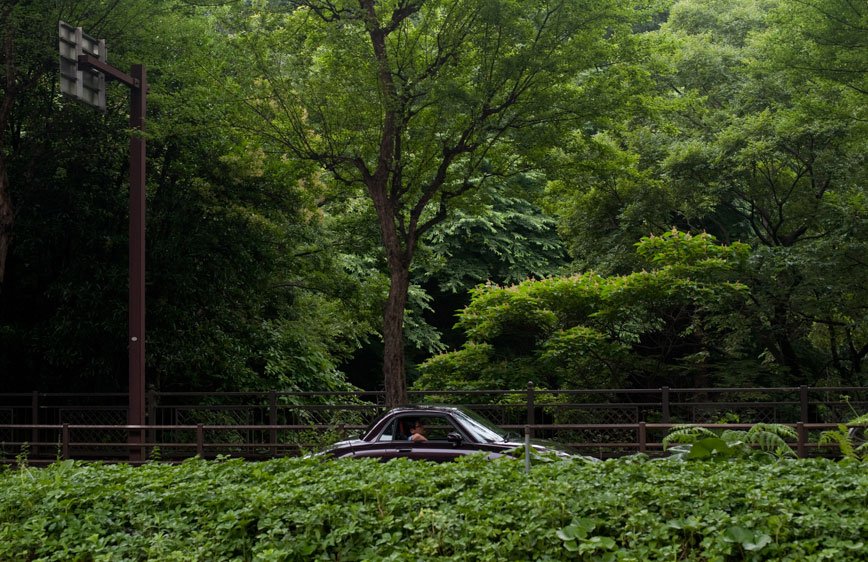
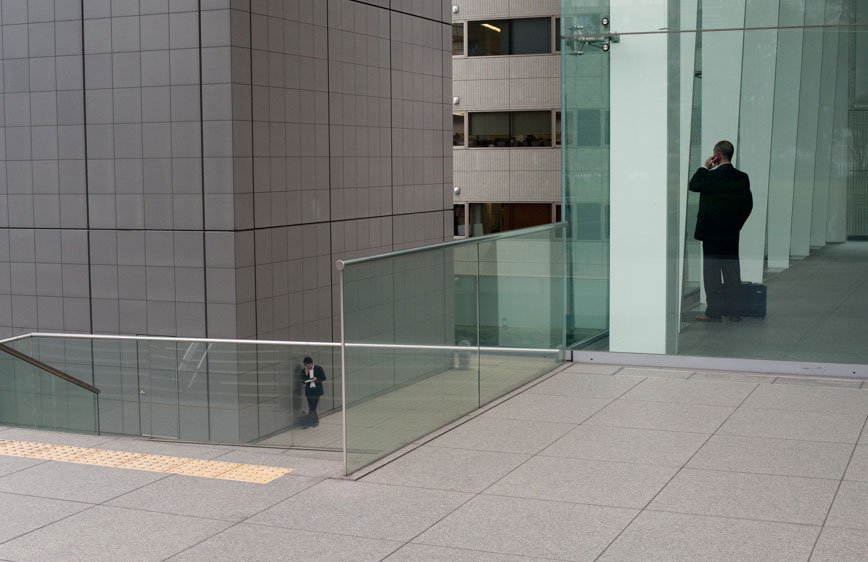
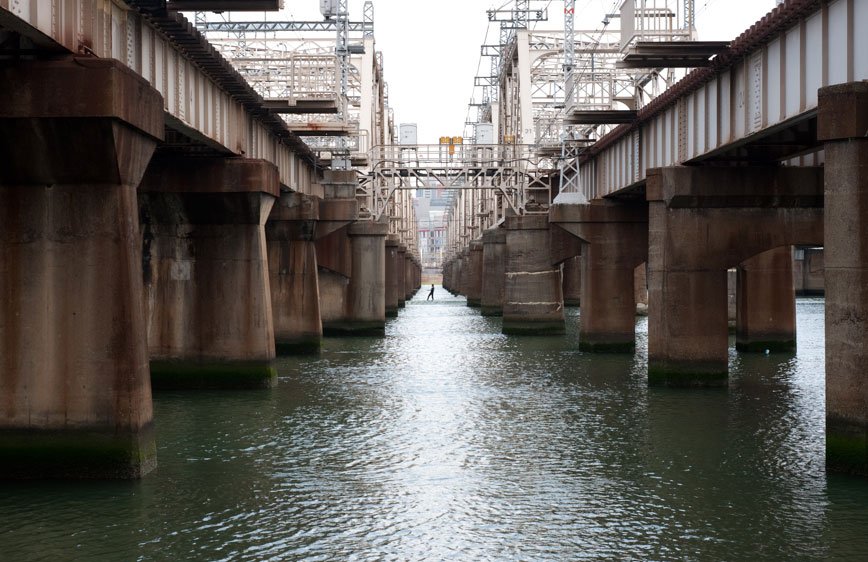
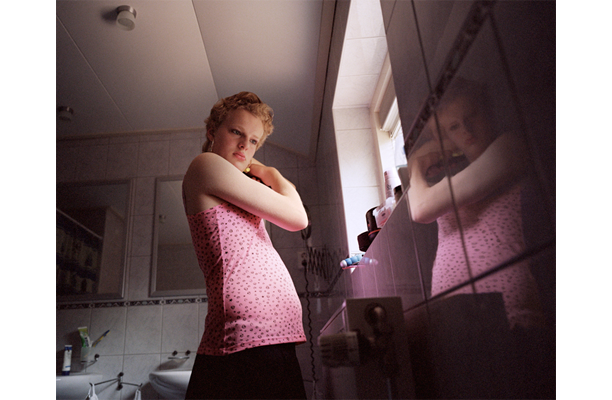
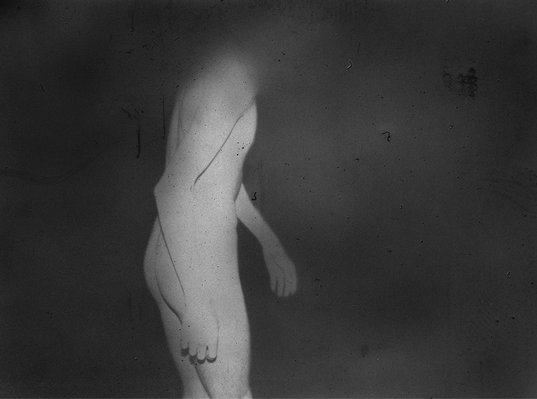
During a brief visit to Japan in 2009 I was soon fascinated by the isolation and loneliness I was feeling in the streets. It started as a personal journey, a foreigner traveling in an alien environment. Language and cultural differences were only augmenting this distance between the locals and me. However, while observing people, it was clear that even indigenous were not able to interact successfully. I have then decided to come back and better visualize these concepts.
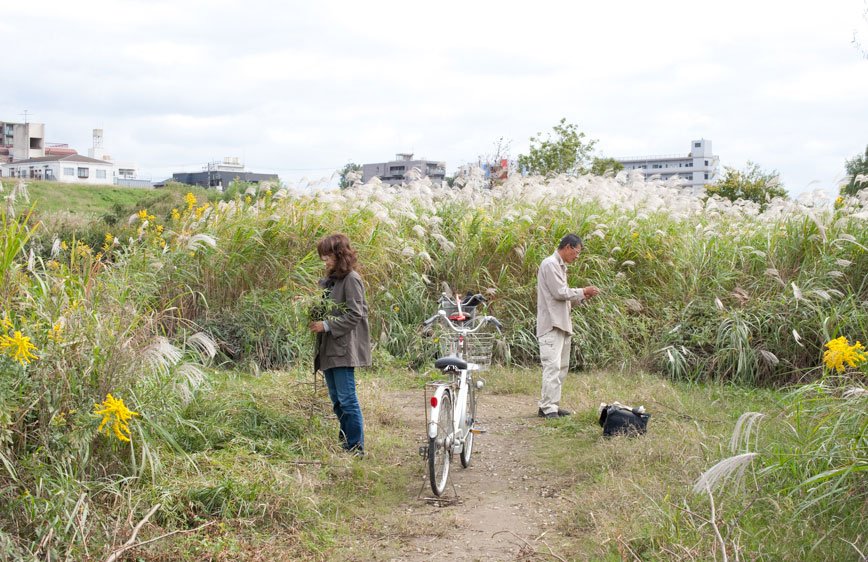
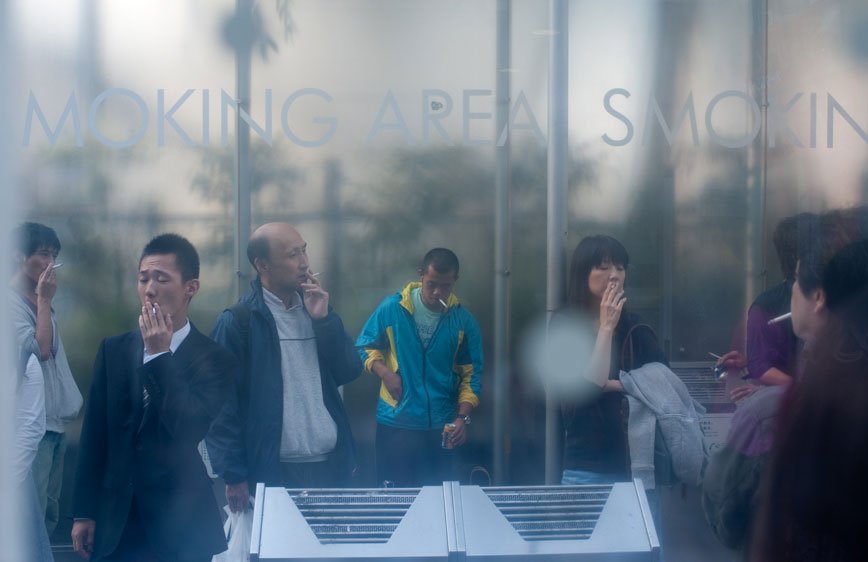
The Tokyo-Nagoya-Osaka Megalopolis, also called Taiheiyō Belt is a unique example of urban agglomeration with an estimated population of over 80 million people. Despite this incredibly high number of chances to interact with people, it seems that society is moving in the opposite direction.
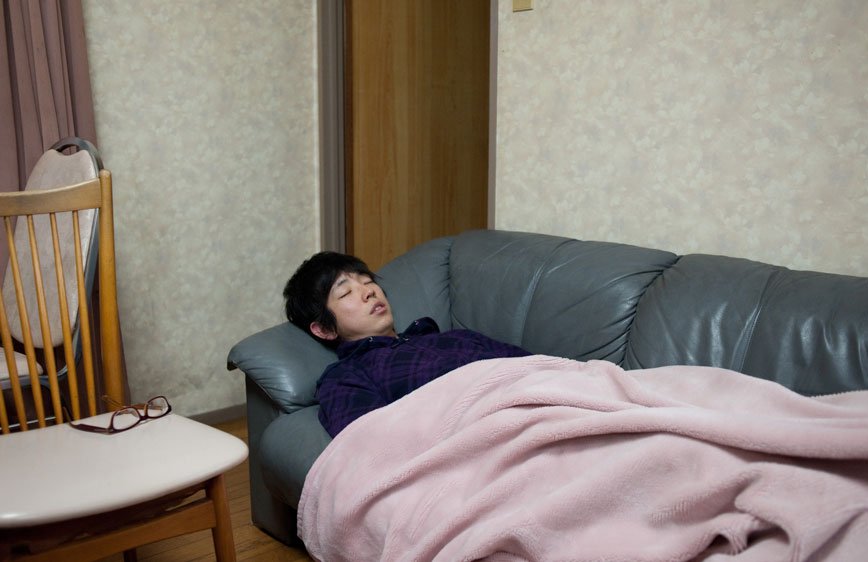
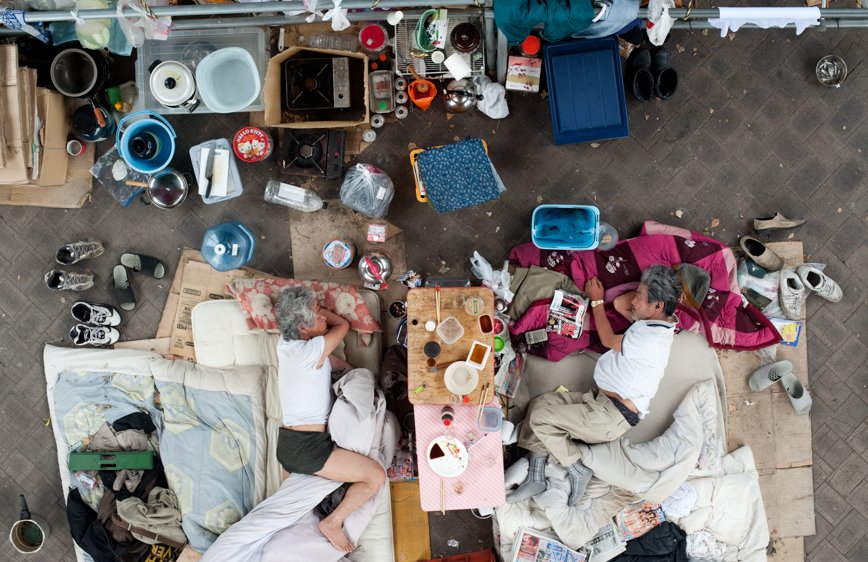
If, in small societies, people have more of an active social role, with multiple connections and greater effect on the community [Eriksen, 2001]; in a larger society some people struggle to communicate with each other, or tend to maintain close contact with only a small number of the closest friends or family members. Some people tend to privilege other communicative systems offered by modern media and communication tools; others have an even more extreme approach. Hikikomori (“pulling away, being confined”) is an acute social withdrawal phenomenon; a Japanese term that defines reclusive people who have decided to socially isolate themselves for periods longer then six month; often these time periods can be counted in years or even decades. It is estimated that 1% of the Japanese population may be Hikikomori. The young people portrayed in this project are all members of Newstart, a NPO working with Hikikomori and NEET (people not in education, employment or training) with the purpose of helping them to re-enter society.
The purpose of this investigation is to create awareness and highlight the problems that modernization and the rapid changes in the environment create in our lives. Is it still important to be, or feel, part of a group? Do we feel part of the environment? Are we alone in the crowd? Support ‘Hitoride’
The Tokyo-Nagoya-Osaka Megalopolis, also called Taiheiyō Belt is a unique example of urban agglomeration with an estimated population of over 80 million people. Despite this incredibly high number of chances to interact with people, it seems that society is moving in the opposite direction.
If, in small societies, people have more of an active social role, with multiple connections and greater effect on the community [Eriksen, 2001]; in a larger society some people struggle to communicate with each other, or tend to maintain close contact with only a small number of the closest friends or family members. Some people tend to privilege other communicative systems offered by modern media and communication tools; others have an even more extreme approach. Hikikomori (“pulling away, being confined”) is an acute social withdrawal phenomenon; a Japanese term that defines reclusive people who have decided to socially isolate themselves for periods longer then six month; often these time periods can be counted in years or even decades. It is estimated that 1% of the Japanese population may be Hikikomori. The young people portrayed in this project are all members of Newstart, a NPO working with Hikikomori and NEET (people not in education, employment or training) with the purpose of helping them to re-enter society.
The purpose of this investigation is to create awareness and highlight the problems that modernization and the rapid changes in the environment create in our lives. Is it still important to be, or feel, part of a group? Do we feel part of the environment? Are we alone in the crowd? Support ‘Hitoride’